Cerebrovascular lay summaries
- BRAIN UK Ref: 21/023 – To understand the pathophysiology of Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities (ARIA)A new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease has recently been approved in the United States (Aduhelm). However, there is a problem with a side effect… Read more
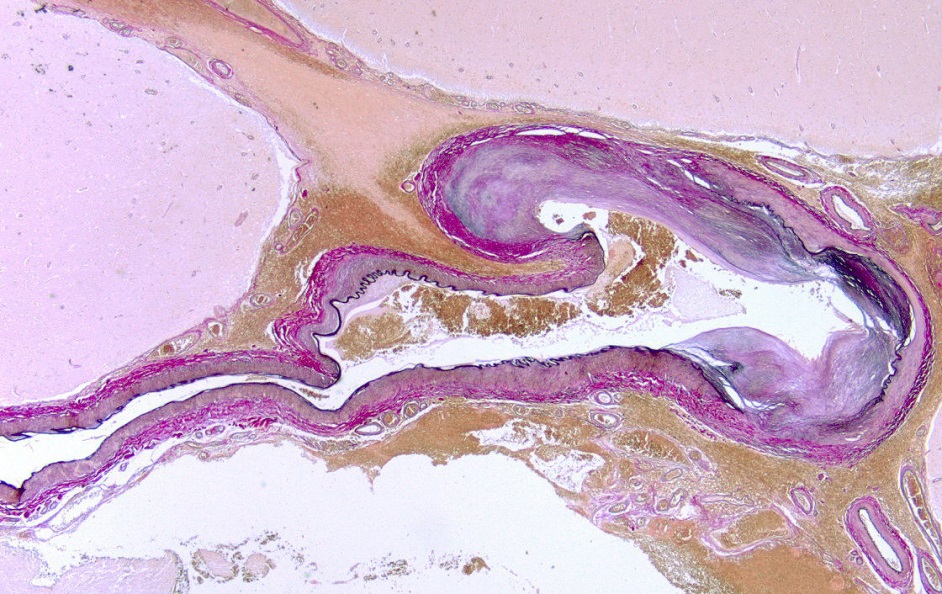
- BRAIN UK Ref: 19/006 – Quantitative analysis of brain vascular pathology in cerebrovascular cases of the Corsellis Brain CollectionThe West London NHS Trust has provided 240 cases of fixed brain tissue from the Corsellis Collection, a historic collection dating from 1950’s to the 1990’s which has now been disbanded. Newcastle will use the tissue to quantify… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 19/004 – Validation of histopathological findings in HTRA1 mutation carriersStroke is the leading cause of long-term disability and the second most common cause of death. In about 20% of cases stroke is caused by changes in small brain vessels… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 17/015 – Inflammatory and vascular changes after brain haemorrhage: A neuropathological assessment of human tissueBleeding into the brain (a brain haemorrhage) happens in 10 to 15% of all strokes. It is also called ICH (intracerebral haemorrhage). When this happens the chances of dying or being disabled are much higher… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 16/006 – Identification of early onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)A proportion of strokes with bleeding into the brain (so-called haemorrhages or haematomas) are caused by the deposition of an aggregated protein called amyloid-beta in the walls of the blood vessels, which makes them brittle, and… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 15/018 – A morphological assessment of the white matter in CAAThe build-up of waste products like amyloid plaques, which are protein pieces, in the walls of arteries is a common cause of stroke and is also commonly observed in Alzheimer’s disease… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 15/004 – Possible ectopic Endothelin secretion in liver cancer resulting in PRESLay summary not available.
- BRAIN UK Ref: 14/017 – Electron microscopic study of CAAThe basement membranes of capillaries and arteries (BM) are the route for the perivascular elimination of amyloid-β, the failure of which is believed to contribute to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 14/001 – CAA and dystroglycanopathiesResearch has implicated the basement membrane (BM) in the route for the perivascular elimination of amyloid-β, the failure of which is believed to contribute to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 13/009 – CAA in autonomic dysfunctionAlzheimer’s disease is an age related neurodegenerative disorder which affects approximately 24%-33% of the Western population aged 85 and above. Symptoms include profound cognitive decline and memory loss, which can often… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 13/007 – CAA in subarachnoid haemorrhageLay Summary not available.
- BRAIN UK Ref: 11/008 – ADAM17 in subarachnoid haemorrhageSubarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding around the brain typically caused by a ruptured blood vessel. A delay in the lack of blood perfusion (ischaemia) is an important determinant in the outcome of SAH… Read more
- BRAIN UK Ref: 11/004 – Response of stem cells in the human brain to acute/hypoxic injuryInjury to the central nervous system through stroke and head injury is common and associated with variable degrees of functional recovery amongst survivors. Tissue damage is mediated by both ischaemia… Read more
